Essential Data Tokenization Best Practices: A Complete Guide
Tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive data with unique identifiers (tokens) that do not inherently have any meaning. Doing this helps secure the original underlying data against unauthorized access or usage. Tokenization was invented in 2001 to secure payment card data and quickly became the dominant methodology for strong security for payment card information. That success, both in terms of market adoption as well as strength of security, prompted exploration of the use of tokenization to secure data other than payment card data. Over the last decade, the use of tokenization for data security has skyrocketed and the industry is now familiar with the strong benefits as well as the numerous limitations of the technology. This blog focuses on data tokenization as it relates to applications beyond payment card data and best practices that enable tokenization users to overcome their typical limitations.
What is tokenization and how does it work?
Tokenization works by replacing underlying original data with unique identifiers or tokens. There are two main categories of traditional tokenization solutions:- Vaulted Tokenization
- Vaultless Tokenization
Vaulted Tokenization
The first type of tokenization is vaulted tokenization. Vaulted Tokenization solutions swap sensitive data with tokens but encrypt and store the original data in a highly secure token vault. When a token needs to be switched back to the original data, it is sent back to the vault, which responds with the original data. Such requests are typically put through proper authentication procedures so that unauthorized requesters are unable to get to the underlying data. Typically token vaults reside in entities that are separate from the entities that are transacting the tokens and this makes the entire architecture very secure.Vaultless Tokenization
The second type of tokenization is vaultless tokenization. Vaultless tokenization solutions swap sensitive data for tokens but do not store the original underlying data. In this type of solution, tokens are generated via token generation algorithms. Depending on whether the application permits tokens derived from the underlying data or not, these systems can use NIST-approved algorithms Format Preserving algorithms (FPE) such as AES FF1 and, less commonly, AES FF3 or proprietary token generation methods that use lookup tables and other such techniques.The Pros and Cons of Tokenization
As with many other data security technologies, traditional methods for Data Tokenization have their pros and cons. This section briefly outlines some of the major pros and cons of traditional Data Tokenization.Pros of Traditional Data Tokenization Solutions
What are the advantages of tokenization? Traditional Data Tokenization Solutions offer the following benefits:- Strong data security
- Several vaultless tokenization solutions offer format-preserving tokens. When properly utilized, these enable applications to work as they did before without modifications
Cons of Traditional Data Tokenization Solutions
What are the disadvantages of tokenization? Traditional Data Tokenization Solutions present the following challenges:- Data Tokenization renders the underlying data completely unusable for any type of insight or analytics. It cannot be properly mined for insight as it cannot be subject to full-featured search or manipulation. Unlike payment card data which is never deeply analyzed, regular data in organizations is the lifeblood of decision making and since the process of tokenization impacts its usability, most organizations elect to not tokenize most of their sensitive data.
- Data Tokenization introduces latency in the overall architecture. Unlike payment card tokenization, where entire transaction flows can take place using tokens, when organizations apply data tokenization, they need to make a lot of calls back and forth to detokenize in order to actually use the data. Large processing times and overheads make tokenization less useful for high-performance use cases.
Best Practices for Data Tokenization Overcome Traditional Limitations
This section outlines general best practices for tokenization and also specifies what organizations can do to overcome the severe limitations of traditional data tokenization solutions.1. Overcome data usability limitations by using Data Tokenization Solutions that permit search and analytics without detokenization
Modern Tokenization Solutions such as Portal26 do not force data detokenization if the underlying data is needed for search and analytics. Portal26 uses high-performance NIST FIPS 140-2 certified searchable encryption inside the token vault and this allows it to accept complex and full-featured queries inside the vault itself. Portal26 can also accept full data and document context inside the vault, which enables a Portal26 Data Tokenization Vault to secure all types of enterprise data without interfering with typical data usage. As as data tokenization vendor, Portal26 offers both Vaulted and Vautless data tokenization solutions. Find Out More >2. Overcome application modification issues by using format preserving tokens: Several tokenization solutions offer format preserving tokens
Organizations should use these to enable use cases where applications or databases cannot withstand changes in data format or the organization is unable to make changes to the underlying application or database. FPE or Format Preserving Tokens are typically offered by Vaultless Tokenization Solution providers though this is an artificial limitation. Portal26 offers format-preserving tokens for both Vaulted and Vaultless Tokenization options. Portal26’s Vaulted Tokenization is offered through our Portal26 Vault Module, whereas the Vaultless Solution is offered through our Portal26 Translation Service Module. Find Out More >3. Overcome high costs of deployment by using a platform that offers different deployment and architecture options
Typically tokenization solutions require major modification to the enterprise’s architecture so that vaults can be deployed and applications/databases can switch out data for tokens. It becomes even more complex when data needs to be retrieved since queries now have to have multiple steps where the first step retrieves the token and the second step swaps the token for the underlying original data. Next Generation Tokenization Solutions like Portal26 offer four different modules that can tokenize data. Customers can deploy a vault, plugin, proxy, or call our translation service to implement data tokenization. Regardless of the option used, Portal26 provides rich data tokenization functionality while still preserving full data usability.4. Apply strong encryption to the token vault
It is important to properly secure the token vault. All encryption should be NIST-certified and organizations could consider the benefit of purchasing a fully certified tokenization solution rather than building their own. Portal26 modules are all fully NIST FIPS 140-2 certified and individual encryption algorithms are also NIST CAVP certified.5. Expand data tokenization to cover all types of sensitive data
With all the capabilities now available in next-generation tokenization solutions like Portal26, enterprises can now apply tokenization to secure all types of valuable data, including data that needs to be manipulated and analyzed. Portal26 typically improves tokenization coverage to 20X of what traditional solutions are able to provide.6. Regularly review and update tokenization policies to meet compliance requirements
Data Tokenization is a strongly recommended data security control for PCI, HIPAA, GDPR, FedRAMP and many other regulations and frameworks. Data Tokenization coverage and access policies should be regularly reviewed to ensure ongoing compliance.Portal26’s Data Tokenization Solutions
Portal26’s Vault is built for high-performance, petabyte-scale analytic use cases and enables full-featured search and analytics without any decryption or detokenization. This makes the Vault and all downstream systems utilizing vault data immune to insider threats and all data-related cyberattacks, including double extortion ransomware. With advanced capabilities, such as structured data analytics with full context, encrypted voice manipulation, and sensitive document text search, our data vault is the most comprehensive data security solution yet. In addition to delivering sophisticated data security, the Portal26 Vault is a game changer for privacy teams as well. With its ability to release data in all nine privacy-preserving formats, support for the granular privacy policy, and in-depth reporting, Portal26 eliminates the need for multiple traditional point solutions. The Portal26 Vault delivers far beyond traditional tokenization and can be used for tokenization of data in three powerful ways.The Benefits of Tokenization with Portal26
- First, customers can use Portal26’s Vault as a standalone solution to store and analyze valuable data without decryption.
- Second, the Vault can also be used as a companion data store for existing applications where sensitive data is transparently isolated into the Vault while retaining the primary DB for other types of data.
- The third and most powerful use of Portal26’s Vault is to build ground-up systems that are natively immune to data compromise.
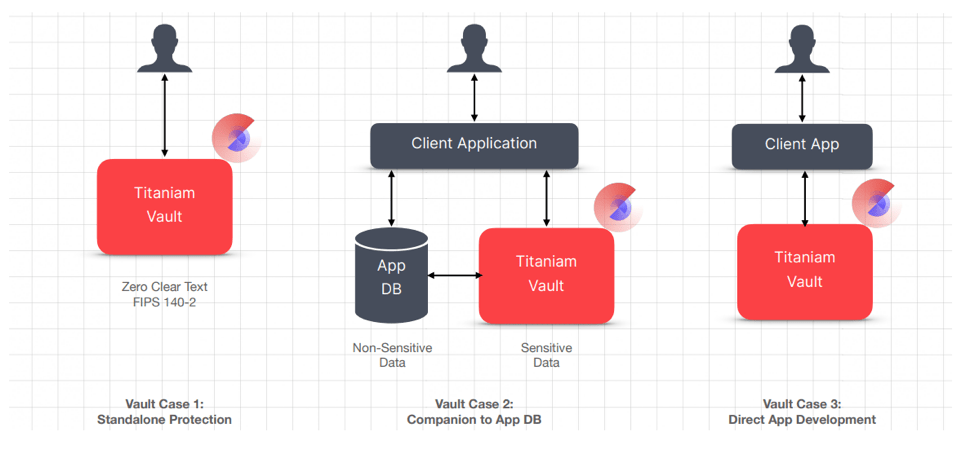 All Vault functionality is exposed via API-based interfaces and the Vault comes natively integrated with the entire Portal26 suite, which expands its protection far beyond the reach of traditional data security and other tokenization solutions.
Explore Portal26 Vault >
All Vault functionality is exposed via API-based interfaces and the Vault comes natively integrated with the entire Portal26 suite, which expands its protection far beyond the reach of traditional data security and other tokenization solutions.
Explore Portal26 Vault >
Conclusion
Data Tokenization is a strong and highly recommended control to keep sensitive data safe from cyberattacks, and inside threats and to meet compliance and data privacy requirements. Next Generation Tokenization solutions such as Portal26 help enterprises get all the benefits without losing data usability or enduring long and complex deployments. Speak to our team or book a demo to find out more. Schedule a Demo >Related Resources

Data States Security Experts Unhappy With Traditional Tokenization
Data States Security Experts Unhappy With Traditional Tokenization Cybersecurity experts may look to Portal26 for all the benefits of traditional tokenization and none of the

Best Practices in Data Tokenization
Essential Data Tokenization Best Practices: A Complete Guide Tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive data with unique identifiers (tokens) that do not inherently have
